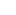
Porosity in High Pressure Die Casting
High pressure dies casting is one of the most economical and fastest ways of making big volumes of products in aluminum, magnesium, or zinc. Die casted parts are known for minimal material wastage, maintenance of consistent features, excellent surface finishing.
High pressure die casting mostly used in a wide variety of industrial applications such as the manufacture of appliance parts, motor housing, heat sinks, engine blocks, and a wide range of commercial and industrial products.
For those intending to create parts and products using high-pressure die casting, you must be comfortable with porosity issues arising in your projects. It's an uncontrollable and unavoidable fact, to reduce such issues we are going to briefly look at its causes and ways you can mitigate against it.
What is Porosity?
Porosity is commonly known as a void or hole in a solid casted metal product or part. The pores can differ in sizes ranging from micropores to much large rand huge holes which are usually measured in cubic millimeter or even larger.
Not only do the pores have to be circular but they also come in the form of irregular linear cracks. There are two main underlying causes of porosity: gas porosity and solidification shrinkage. For this post, we are going to closely look at these two causes and discuss ways in which we can mitigate them.
Solidification Shrinkage
When the molten material is injected onto the mold cavity, solidification begins immediately when they come into contact with cooler walls This solidification will cause shrinking of the solidified part, but the shrinking rate is solely dependent on the tooling mold geometry as well as the alloy being used.
The semi-liquified section of the metal that is far from the mold tool wall is referred to as slush, this is the part where pores are likely to be formed. Additionally, when the molten materials solidify it blocks all liquid passages to other sections within the mold, this will lead to the creation of pores as a result of lack of complete liquification of all the features within the design.
Gas Porosity
Gas pockets can form in the following ways, this is the case the hydrogen or aluminum falls out of the suspension and seal it with hydrogen gas. The air pocket can also get trapped in the mold tool when its bot is fully vented or evacuated.
The gas porosity vaporizes forming bubbles, the liquids, and oils which will not evaporate will emit contaminants which can be included in the final part.
How to Prevent Porosity?
wall thickness
One of the fastest and easiest ways of tackling porosity is the maintenance of wall thickness, this is the job of a mold tool designer.
shrink rate
It's a wise investment decision that a client or manufacturer works closely with high pressure die caster and discusses various options of the raw-materials based on the design and application.
It's always best to be on the same page with the manufacturers to get everything clear when it comes to the specifications and ideas at the early stages of product development to avoid issues arising from porosity.
Search
Recent Posts
Categories
Archives
- Apr 2024
- Mar 2024
- Feb 2024
- Jan 2024
- Dec 2023
- Nov 2023
- Oct 2023
- Sep 2023
- Aug 2023
- Jul 2023
- Jun 2023
- May 2023
- Apr 2023
- Mar 2023
- Feb 2023
- Jan 2023
- Dec 2022
- Nov 2022
- Oct 2022
- Sep 2022
- Aug 2022
- Jul 2022
- Jun 2022
- May 2022
- Apr 2022
- Mar 2022
- Feb 2022
- Jan 2022
- Dec 2021
- Nov 2021
- Oct 2021
- Sep 2021
- Aug 2021
- Jul 2021
- Jun 2021
- May 2021
- Apr 2021
- Mar 2021
- Feb 2021
- Jan 2021
- Dec 2020
- Nov 2020
- Oct 2020
- Sep 2020
- Aug 2020
- Jul 2020
- Jun 2020
- May 2020
- Apr 2020
- Mar 2020
- Feb 2020
- Jan 2020
- Dec 2019
- Oct 2019
- Sep 2019
- Aug 2019
- Jul 2019
- Jun 2019
- May 2019