Silicone rubber molding is a versatile manufacturing process used across industries—from medical devices and automotive components to consumer electronics and aerospace. Recent advances in materials, automation and sustainability are transforming the way silicone parts are produced. This article explores the latest trends, techniques and applications in silicone rubber molding.
Advancements in Molding Technologies
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Injection Molding:
Enhance production speed, accuracy and repeatability. Innovations include multi-material molding and high-temperature mold designs for complex geometries.
Compression Molding:
Improvements in mold design and automation have resulted in increased efficiency, reduced waste, and expanded application scope.
Additive Manufacturing Integration:
3D printing of molds and prototypes accelerates development cycles and allows for complex, custom designs that would be difficult to produce with traditional methods.
Material Innovations
High-Performance Silicone Formulations:
The development of heat-resistant, UV-stable and chemically resistant silicones has broadened the range of applications to include automotive, aerospace and medical devices.
Eco-Friendly and Low-Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Silicones:
Focus on sustainability with formulations that reduce environmental impact and improve safety during processing.
Nano-Enhanced Silicones:
Incorporation of nanomaterials improves mechanical properties, thermal conductivity and electrical insulation.
Design and Process Optimization
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Simulation:
Advanced software enables precise mold flow analysis, defect minimization, and pre-fabrication optimization of part designs.
Automation and Robotics:
Increased use of automated systems for material handling, mold loading/unloading and quality inspection enhances consistency and reduces labor costs.
Smart Molds and IoT Integration:
Sensors embedded in molds monitor temperature, pressure, and cycle times, enabling real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance.
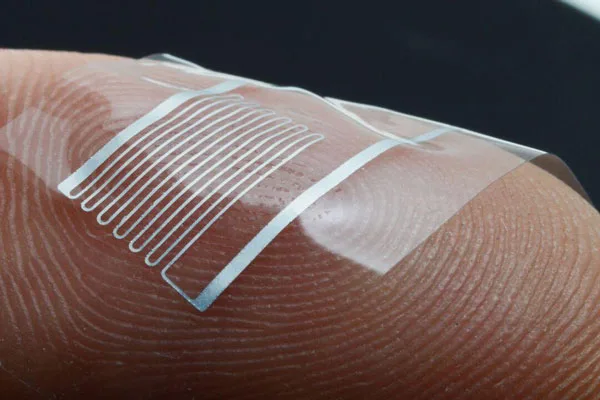
Stretchable electronics
Emerging Applications
Medical Devices:
Silicone’s biocompatibility and flexibility are leveraged in implants, seals and wearable devices, with innovations focused on sterilization and biocompatibility enhancements.
Wearable Technology:
Silicone molds are used for flexible circuits, sensors, and protective housings in consumer electronics.
Automotive and Aerospace:
High-performance silicones withstand extreme conditions, and molded components are used in seals, gaskets and insulation systems.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Recycling and Reprocessing:
Develop methods for recycling silicone scrap and waste to promote circular economy practices.
Energy-Efficient Processes:
Innovations in mold heating/cooling systems have reduced energy consumption during the molding cycle.
Future Outlook
Hybrid and Multi-Material Molding:
Combine silicone with other polymers or materials to create multifunctional components.
Nanotechnology Integration:
Further exploration of nanomaterials to enhance the properties of silicone is beyond current capabilities.
Customization and Small Batch Production:
Emphasis on rapid prototyping and low-volume, highly customized parts driven by digital manufacturing trends.
Conclusion
The silicone rubber molding industry is poised for continued growth, fueled by technological innovations, material improvements and a focus on sustainability. Keeping abreast of these trends enables manufacturers to produce higher quality, more complex and environmentally responsible silicone components that are suited for a wide array of advanced applications.
